In most people, nails and skin are affected by fungus, which does not look very pretty. It is important to understand that this is not only an aesthetic, but primarily a medical problem.
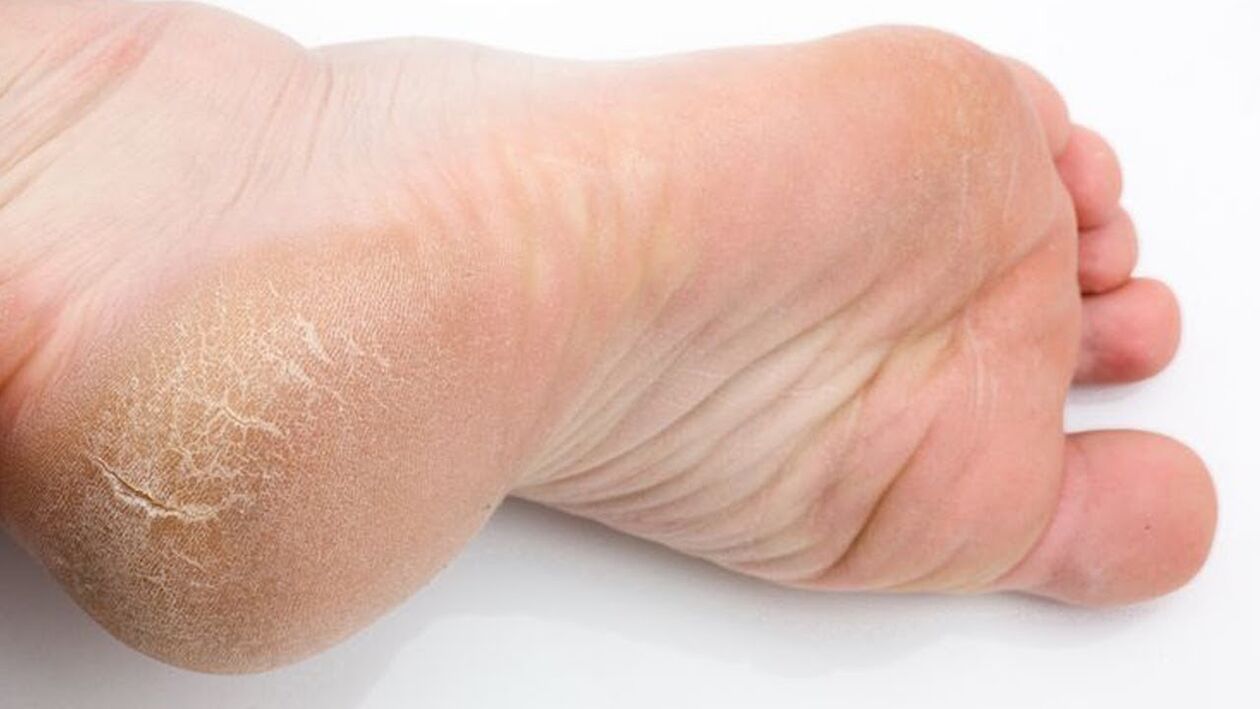
In some cases, fungal skin lesions can be a sign of a serious illness, such as diabetes. Do not start the disease, because the treatment process on average takes a year or more.
How can you get skin and nail fungus?
More than 40 species of various parasitic fungi (dermatophytes) are known that can affect the skin and nails. The most common are representatives of the genus Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. For growth and reproduction, they use a special substrate - keratin, which consists of the top layer of skin (epidermis), hair and nails. Penetrating into the epidermis or nail plate, the fungus is installed there, begins to grow and multiply.
You can be infected from a sick person, through objects (towels, wooden shelves in bathrooms, saunas, carpets, benches in public pools, manicure / pedicure tools) and contact with the ground if you like to walk barefoot.
At -risk groups
The most common types of fungal diseases include mycosis of the skin of the feet and onychomycosis of the nail plate. From the moment of infection until the appearance of the first clinical symptoms, it takes from a few weeks to several months.
More often than others, men suffer from fungal diseases. Among women, those who regularly wear pointed shoes, especially high heels, are more likely to develop the disease. In this case, the toes are constantly flattened, which leads to friction, small wounds, abrasions, which are the entrance to infection.
You can also "catch" fungus in a regular beauty salon during a pedicure procedure if the master uses improperly processed tools. To remove spores and fungal debris from metal surfaces of clamps, scissors and tweezers, the tool must be sterilized in a dry heat cabinet. Not all salons have such equipment, so they are limited to "soaking" in a disinfectant solution and "drying" in an ultraviolet box. This treatment does not completely protect against infection.
Frequent participation of fungal infections can signal the development of diabetes. According to statistics, diabetics are three times more susceptible to mycosis. Fungus can also appear with allergic skin lesions (itching, inflammation, crying), brushing insect bites, while taking antibacterial drugs, corticosteroid hormones, antidepressants.
Athlete's foot symptoms
- Dry, cracked, flaky skin in the interdigital folds.
- Itching.
- Hyperkeratosis (thickening of the skin of the feet).
- Enlargement of the lesion.
- In some cases, staphylococcal infections accompany fungal infections, which are relatively difficult to cure.
Symptoms of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Among all nail diseases, onychomycosis accounts for up to 40%. Dermatophytes account for up to 90% of all fungal nail infections. The most common pathogen is a fungus of the genus Trichophyton.
The appearance of fungus in this case may be preceded by injury to the nail or constant softening of the nail plate due to high humidity. This, for example, can be done when wearing the same pair of shoes / boots every day.
As the infection progresses, the color of the nail changes - part of the nail becomes yellow, gray or whitish. Over time, the spot grows, and the nail itself thickens - the development of subungual hyperkeratosis occurs.
Diagnosis of fungal diseases
For the diagnosis of fungal infections and onychomycosis, special tests for fungal detection are used. Biomaterials (hair fragments, nail plates, skin particles) were analyzed under a microscope. If an infection has occurred and mycelial threads (fungal bodies) are visible, the diagnosis is confirmed.
If microscopic examination gives an ambiguous answer, then bacteriological examination is carried out - sowing the material on the fungus. This test allows not only to identify the infection, but also to determine the sensitivity to antifungal drugs, which is necessary for the selection of effective treatment.
How to protect yourself from fungus
- Dry your feet after a shower or bath, especially between the toes.
- If you wear closed shoes, change your socks/socks daily.
- Change shoes every two to three days, don’t wear the same pair every day.
- Do not walk barefoot in public places (swimming pools, baths, saunas, fitness clubs).
- If someone in your family has a fungal disease, give him or her a separate set of towels and linens. Wash them separately at the highest temperature.
- If you have fungus on the same foot or nail, use two different sets of manicures/pedicures to prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas.
- If you have diabetes, control your blood sugar levels. "High sugar" reduces the rate of wound healing on the skin ("diabetic foot"), which facilitates access to fungal infections.
Be healthy!
















